contents: 0-1. CA Intro
Addition & Subtraction
Addition: just do the binary addition with given numbers
Subtraction: do the binary addition with the negation of the second operand
Half adder
1-bit adder without carry-input
-
Input: two one bit-data A, B
-
Output: sum(S), carry(C)
Full adder
1-bit adder with carry-input
-
Input: two one bit-data A, B, carry(C)
-
Output: sum(S), carry(C)
Circuit design for addition and subtraction
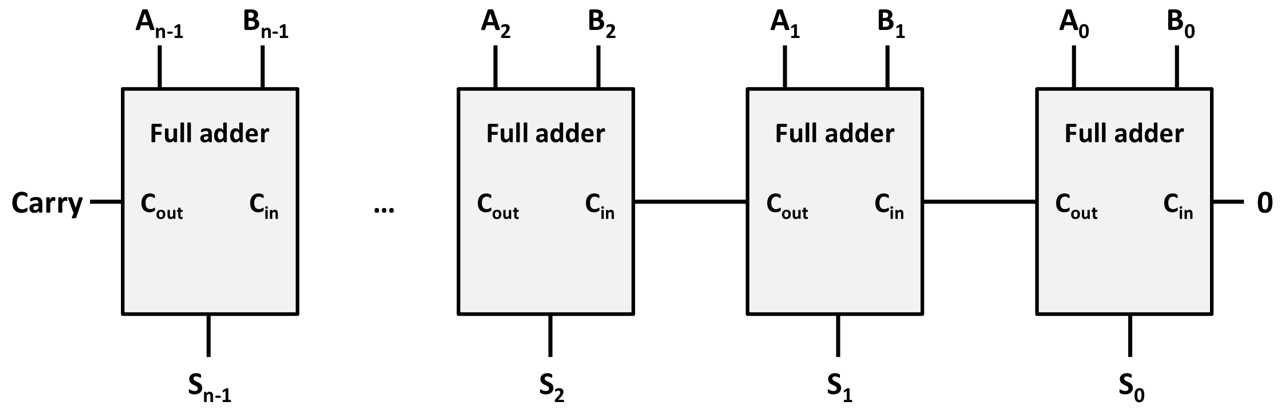
N-bit parallel binary adder
-
Initial carry input is 0
-
The i-th adder waits for the carry until it is generated by the (i-1)-th adder
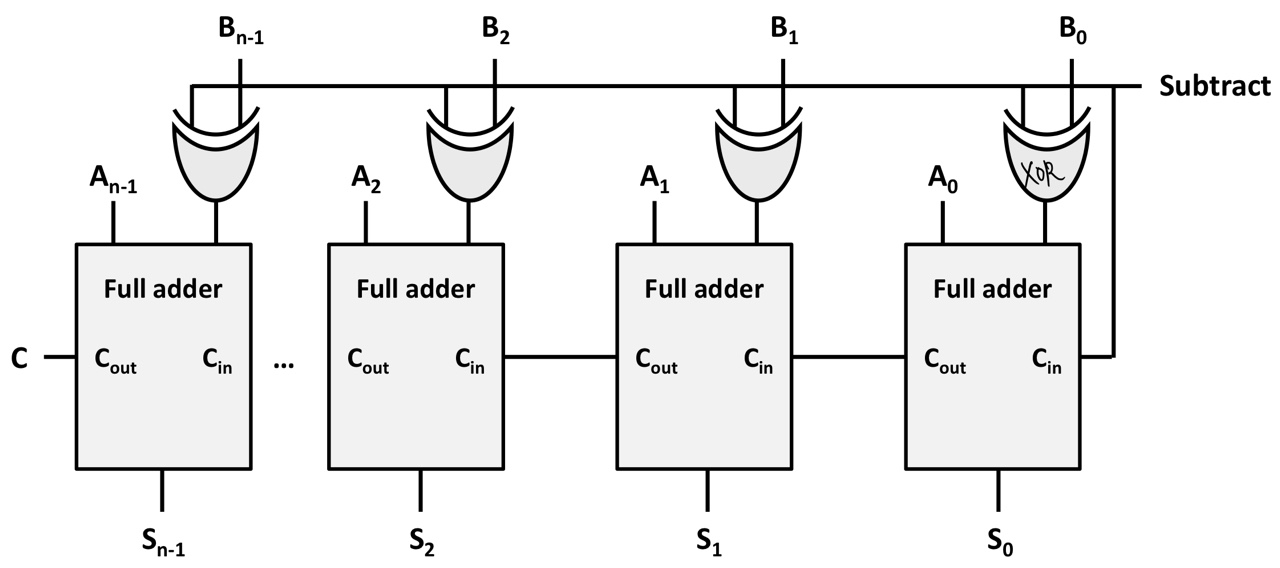
Adder with subtraction (in two's complement)
-
Subtract = 0 or 1 (if subtract == 1, B is inverted)
-
Subtract is also added as the initial carry (if subtract ==1, 1 is added)
Overflow
Overflow occurs when computation results are too large (out of range)
When does it occur?
-
Add two positives or negatives + the sign of result is different with sources
-
Subtract a negative from a positive + the sign of result is 1
-
Subtract a positive from a negative + the sign of result is 0
How to detect Overflow?
-
Use
add, addi, subinstructions -
They cause exceptions on overflow
- A program jumps to predefined exception handler address
-
e.g., Fortran does not allow overflows. So MIPS Fortran compilers always use
add, addi, sub
How to ignore Overflow?
-
Use
addu, addui, subuinstructions (u means unsigned) -
They do not cause exceptions on overflow
-
e.g., C ignores overflows. So MIPS C compilers always use
addu, addui, subu